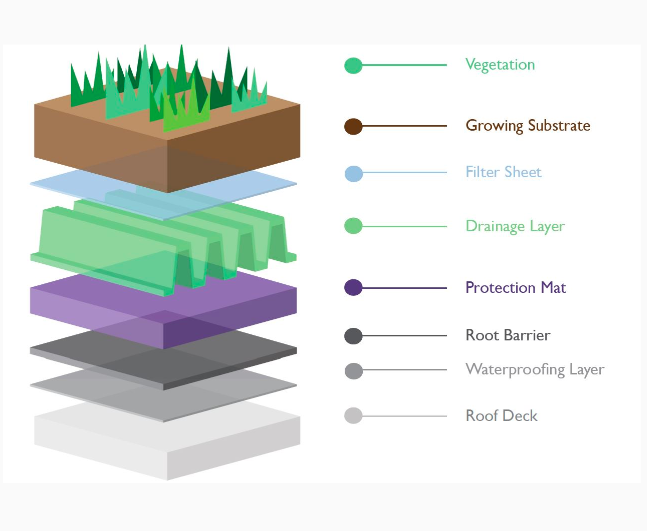
SDH Green Roof
The SDH Green Roof team worked to design a green roof for the Sustainability Demonstration House. This included calculating the expected snow loads, the total load of the different layers, cost estimates, and researching potential vegetation.
Forestry Waste Audit
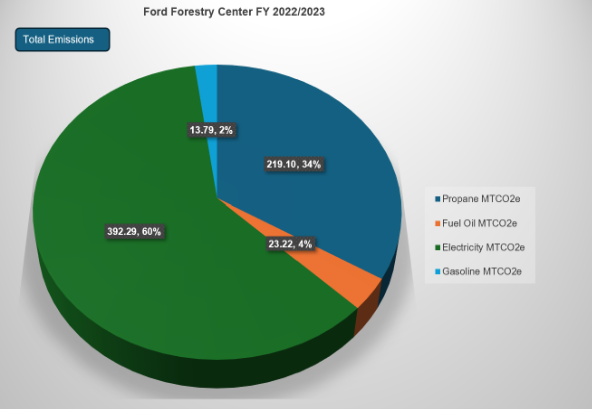
The Forestry Waste Audit team assisted CFRES in reducing their waste by performing a waste audit on all the forestry buildings around campus. The team is also assisting in the creation of a sustainability plan to support the college-wide sustainability effort.
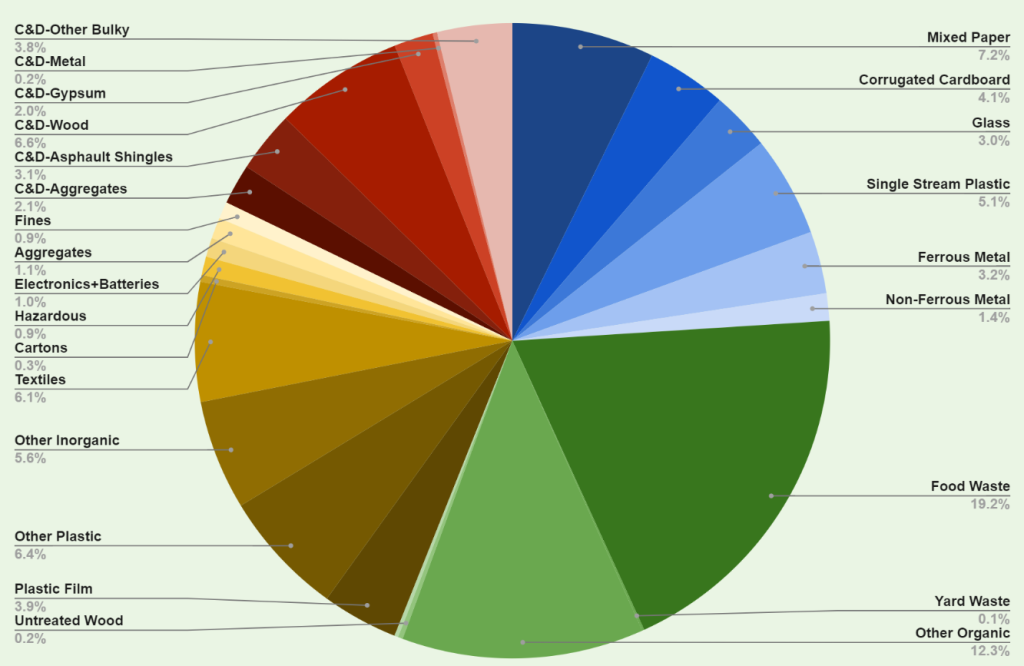
Houghton County Waste Characterization Study
Worked to determine the composition of waste that is disposed of in Houghton and Keweenaw Counties. Knowing what is in the waste (eg. food waste, paper products, metals, textiles) can help to make evidence based decisions on the kind of sustainable solid waste infrastructure decision makers in Houghton County should invest in.
Net Zero Tiny House Build
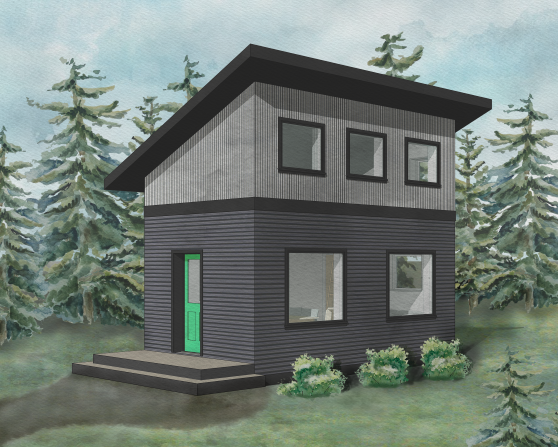


The Tiny House Build Team was tasked with designing and building a tiny house as a sponsorship with Paul Sanders on a property in Bete Grise off of Lake Superior.
The Tiny House Build project began with a goal of designing a sustainable and affordable tiny house for cold climates, like in the Upper Peninsula, to provide a model for green, energy-efficient housing. The team began researching and developing innovative solutions for making common building practices more sustainable, in addition to modeling thermal and energy performance of the team’s preliminary tiny house designs. Once the best option was modeled, students worked directly with the client to create construction drawings to bring the house from an idea to reality. The team constructed sections of the tiny house on campus. When complete, they installed them on the client’s property, where the house was fully finished and move-in ready. Finally, the team conducted testing to determine the success of the chosen design in terms of energy-efficiency and thermal performance.
Solar Thermal
Several years ago, Green Campus Enterprise was tasked with determining the feasibility of using solar thermal collectors to reduce Michigan Tech’s stationary emissions. The Solar Thermal team was created to work on this project with the goal of calculating the solar thermal potential in the Houghton climate and to look for potential areas of implementation on the Michigan Tech campus. The purpose of a solar thermal system is to harvest the sun’s energy by passing sunlight through a collection system which converts solar energy to heat. This heat is then used to warm fluids for different applications throughout the University and reduce the amount of fossil fuels needed for the heating process.
Wind Energy

The Wind Energy Team of the Green Campus Enterprise is focused on preparing a feasibility study for putting a wind turbine on Michigan Tech’s campus. The team has decided on a location at the top of Mt. Ripley, and a 100kW turbine. Currently, the team is completing a financial analysis to determine the payback period on this turbine. The team has used OpenWind software to obtain capacity factors, which provide information on how efficient the turbine will be. These capacity factors are used in conjunction with the cost of energy to complete a cost analysis.
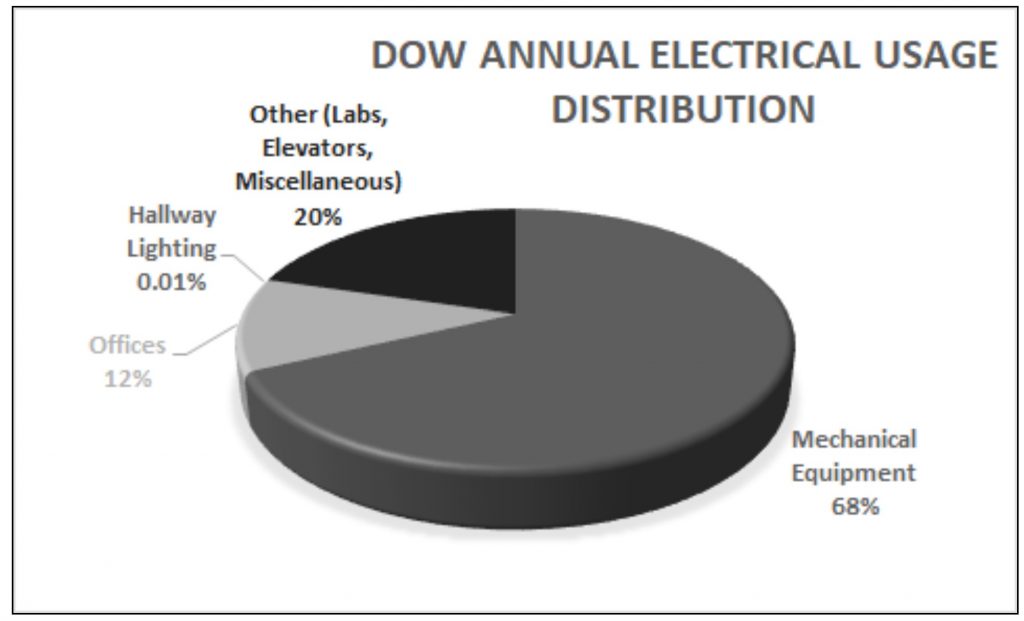
High Rise
The High Rise Buildings Project was created in 2014 under the initiative of Dave Taivalkoski who asked Green Campus Enterprise if there was an interest in forming a student team dedicated to investigating the annual electricity usage of the DOW Environmental Sciences and Engineering Building. The project was proposed with the intent of identifying a probable cause for excess electrical energy consumption. The project continued until 2018.
GLRC Cooling Water Retrofit
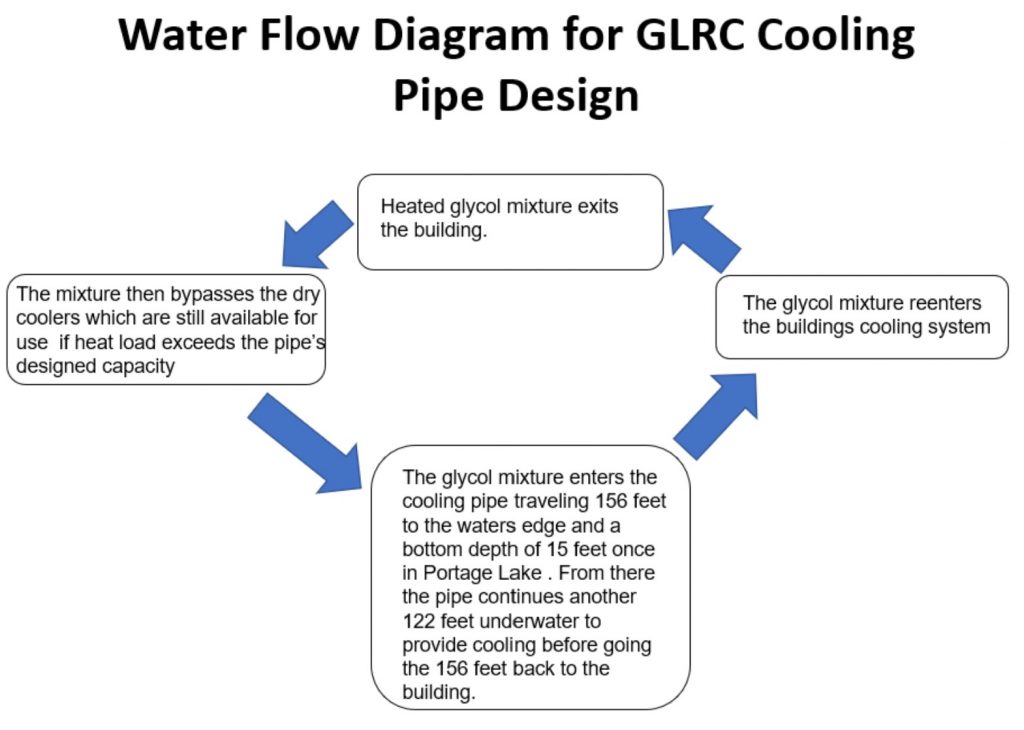
Members of the Green Campus Enterprise on Michigan Tech’s campus have designed a system to dissipate excess heat from the Great Lakes Research Center (GLRC) into the Portage Canal. The GLRC currently has a system of dry-coolers to dissipate this excess heat from the building. The new design saves the University about $20,000 a year on electricity needed to run the current dry cooler system, and has a pay-back period of about three years.
